Most causes of hair loss in men can be attributed to one of the following reasons:
- Male pattern baldness (Androgenetic Alopecia)
- Hereditary (family history of hair loss)
- Medical conditions and medications
- Changes in your hormones
- Scarring from accidents, surgery, and chemical/thermal burns
- Hair loss due to hair pulling (braiding/weaving)
While knowing the cause of your hair loss isn’t going to fix it by itself, recognizing the type of hair loss you have is the first step in determining your ideal treatment plan.
What is DHT?
Dihydrotestosterone (DHT) is an androgen. An androgen is a sex hormone that contributes to the development of what are thought of as “male” characteristics, such as body hair. But it can also make you lose your hair faster and earlier. There are treatments meant to slow the onset of male pattern baldness by specifically targeting DHT.
DHT’s connection to balding
Hair everywhere on your body grows out of structures underneath your skin known as follicles, which are essentially tiny capsules that each contain a single strand of hair. The hair within a follicle goes through a growth cycle that lasts about two to six years. Even if you shave or cut your hair, the same hair will grow back out of the follicle from the root of the hair contained within the follicle.
At the end of this cycle, the hair enters what’s known as a resting phase before finally falling out a few months later. Then, the follicle produces a new hair, and the cycle begins again.
High levels of androgens, including DHT, can shrink your hair follicles as well as shorten this cycle, causing hair to grow out looking thinner and more brittle, as well as fall out faster. DHT can also make it take longer for your follicles to grow new hairs once old hairs fall out.
Some people are more susceptible to these effects of DHT on scalp hair based on variations in their androgen receptor (AR) gene. Androgen receptors are proteins that allow hormones like testosterone and DHT to bind to them. This binding activity typically results in normal hormonal processes like body hair growth.
But variations in the AR gene can increase androgen receptivity in your scalp follicles, making you more likely to experience male pattern hair loss.
Male Pattern Baldness (Androgenetic Alopecia)
As its name implies, male pattern baldness usually displays a predictable pattern, with hair loss beginning at the hairline above the temples and gradually receding. Male pattern baldness is also the most common cause of hair loss in men, accounting for more than 95% of all hair loss cases.
Male pattern baldness causes your hair follicles to shrink slowly over time until they stop regrowing. Without proper attention, it can eventually progress to the point where only hair on the sides and rear of the head is left. With timely treatment, this outcome can be prevented.
Patchy Hair Loss (Alopecia Areata)
Much less common than male pattern hair loss is patchy hair loss and spot baldness, also known as Alopecia areata. Alopecia areata is an autoimmune disease that occurs when your body’s immune system attacks your hair follicles, leaving a smooth, round patch of hairless skin. Patchy hair loss can happen in otherwise healthy people.
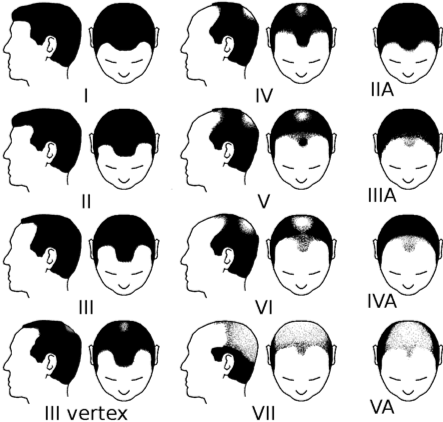
Hair Loss Classifications: The Norwood Scale
Since male pattern baldness is the most common and predictable form of male hair loss, a visual scale was developed by Dr. James Hamilton (and later updated by Dr. O’Tar Norwood) to help men identify the level of their hair loss. Using the Norwood scale as a guide, we can identify your individual hair loss classification. The sooner you address your hair loss, the greater the chance you can preserve or save your hair.
- Class 1 represents a head of hair with no visible hair loss.
- Class 2 is characterized by the beginning of a receding hairline and some recession in the temple region.
- Class 3 patients exhibit a more significant decline in hair above the temples as well as receding from the forehead. In the Class 3 vertex, hair loss is starting to become significant on the crown.
- Class 4 hair loss may become more noticeable on the crown or patients may have significant hair loss above the temples and/or forehead.
- Class 5 hair loss affects the front and back of the scalp, with only a small area of the front hairline remaining and a rather large area of hair loss on the top.
- Class 6 advanced hair loss occurs when the hair bridging the two sides of the head is fading away or completely gone. There may still be sufficient donor hair for transplantation; however, results may be limited.